SIGNAL DETECTION:
In cognitive radio networks, in order to avoid interference form secondary users to the primary license holders of the spectrum, reliable spectrum sensing is necessary. In scenarios where the noise samples are correlated, the spectrum sensing methods optimized considering impairment by independent noise samples will not provide optimum performances.Locally Optimum (LO) detection of random signals under a weakly correlated noise model over fading channels. In practice, simple energy detection is often preferred over more complex detection techniques. Therefore, we try to come up with an LO detection technique with comparable complexity to energy detection for correlated noise environments.
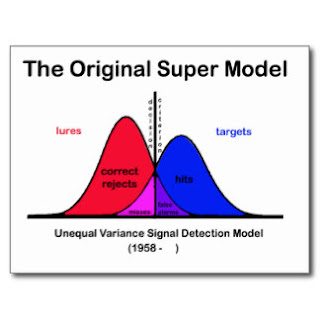
Fig: signal detection
FOR MORE DETAILS
On Signal Detection in the Presence of Weakly Correlated Noise over Fading Channels
In cognitive radio networks, in order to avoid interference form secondary users to the primary license holders of the spectrum, reliable spectrum sensing is necessary. In scenarios where the noise samples are correlated, the spectrum sensing methods optimized considering impairment by independent noise samples will not provide optimum performances.Locally Optimum (LO) detection of random signals under a weakly correlated noise model over fading channels. In practice, simple energy detection is often preferred over more complex detection techniques. Therefore, we try to come up with an LO detection technique with comparable complexity to energy detection for correlated noise environments.
Fig: signal detection
FOR MORE DETAILS
On Signal Detection in the Presence of Weakly Correlated Noise over Fading Channels
No comments:
Post a Comment